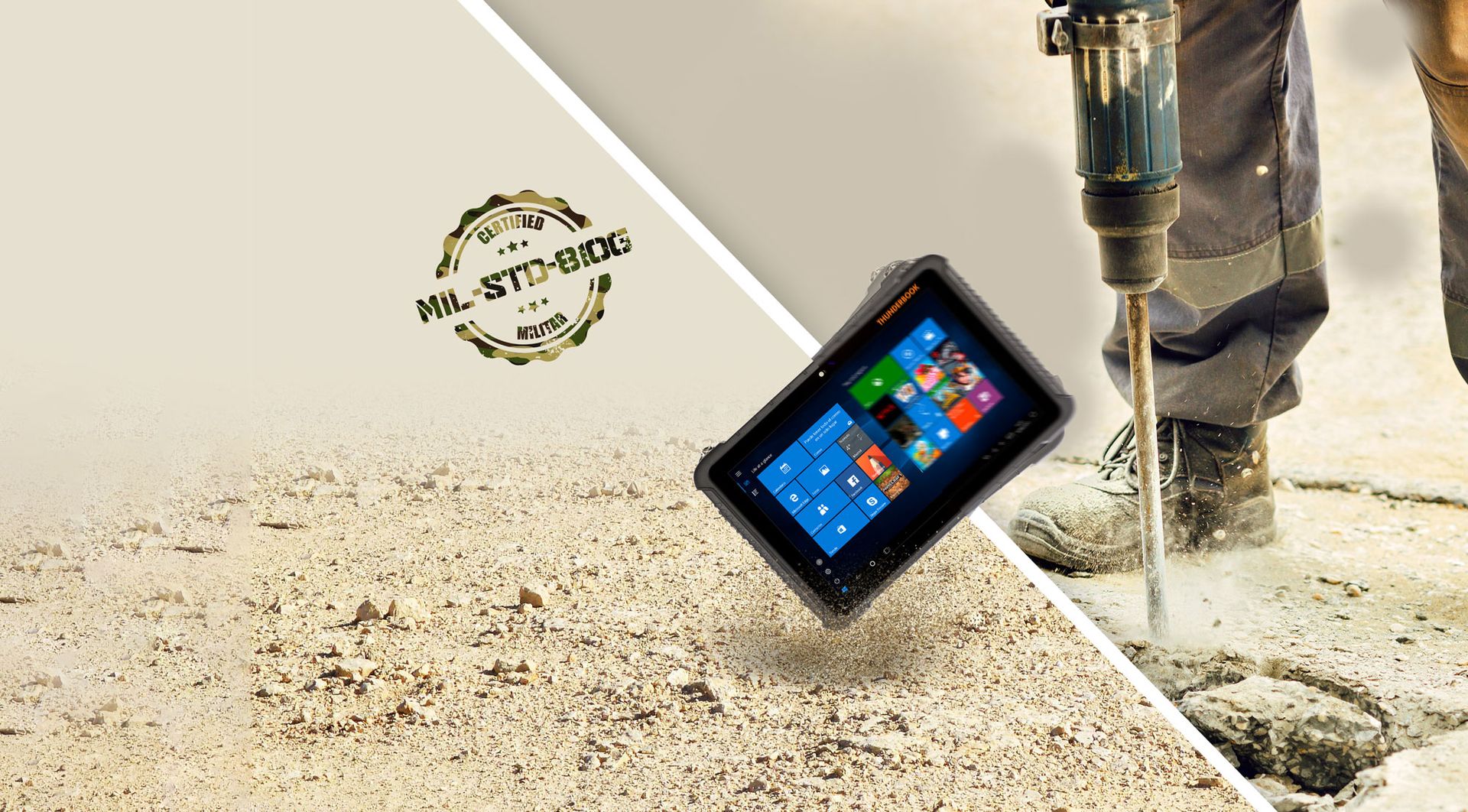
In this post, we’ll explain what guarantees that a tablet is truly rugged. We’ll go over the tests required to obtain MIL-STD 810G and IP certifications, accreditations that prove a device’s resistance in various environments and situations.
You should know that both certifications are complementary but not interchangeable. Make sure your device has both to be 100% sure of its rugged condition.

MIL-STD 810G Resistance Tests
The MIL-STD military certification originated in the U.S. after World War II and was initially used by certain military divisions. Today, it serves as a benchmark for a device’s ability to withstand extreme conditions, under the following parameters (Standard/Controlled Environment):
•Low Pressure (Altitude): Atmospheric pressure – Pressure of the area / barometric pressure – 28.5 +2.0 / -3.0 in Hg
•High/Low Temperature: Temperature – 25° ± 10°C (77 ± 18°F) / –23° ± 2°C (73 ± 3.6°F)
•Humidity: From 20% to 80% / 50% ± 5%
In addition to these value ranges, the tests include other environmental conditions such as:
Temperature Shock
Sudden and extreme temperature changes.
Rain
Protection and performance during and after exposure to water in the form of mist, droplets, or rain.
Immersion
Operation during and after submersion under water.
Dust and Sand
Functional resistance to particles between 150 and 850 μm (micrometers).
Fluid Contamination
Casual, intermittent, or prolonged exposure to contaminating fluids.
Freezing/Thawing
Ability to withstand transitions between solid and liquid states. Includes exposure to ice.
Salt Fog
Effects of salt on the physical and electrical components of the device.
Noise
Device resistance to severe acoustic environments.
Solar Radiation
Effects of heat and sun exposure (photodegradation).
Combined Environments
Operation during a combination of several hostile environmental conditions.
Fungus
Material susceptibility to fungal growth.
Rust
Internal and external maintenance in corrosive and rust-inducing environments.
Additionally, obtaining this certification requires passing a series of impact and movement-related tests:
• Vibration: Device tolerance to vibration over its lifecycle. Includes mechanical vibrations from ships and/or aircraft.
• Acceleration: Performance after inertial load changes caused by deceleration, acceleration, or both.
• Shock: Physical integrity and functionality after shocks from handling, transport, and fieldwork.
• Gunfire: Physical integrity and functionality after exposure to firearm discharge impacts.
• Impacts: Resistance to impacts caused by train collisions, explosive detonations, and abrupt impulse changes.
All these scenarios can be simulated using a “multi-exciter” setup to replicate real-life challenges to the device.
IP Protection Ratings
IP (Ingress Protection) ratings refer to the level of protection against dust, water, and foreign objects. These ratings consist of two digits:
• First digit: Indicates protection against solid objects, including particles as small as dust.
• Second digit: Indicates protection against liquids such as drips, rain, sprays, immersion, and spills.
Below are the levels for the first digit (solid ingress protection):
• Protection against solid objects larger than 50 mm.
• Protection against solid objects larger than 12.5 mm.
• Protection against solid objects larger than 2.5 mm.
• Protection against solid objects larger than 1.0 mm.
• No ingress of dust in quantities that could interfere with normal operation.
• Completely dust-tight.
As for the second digit (liquid ingress protection):
• Protection against vertically dripping water while the device is upright.
• Protection against dripping water when tilted up to 15 degrees.
• Protection against water spray at angles up to 60 degrees from vertical.
• Protection against splashing water from any direction.
• Protection against water jets from a 6.3 mm nozzle at 12.5 L/min.
• Protection against powerful water jets (12.5 mm nozzle at 100 L/min).
• Protection against immersion in water up to 1 meter deep for 30 minutes.